As the US economy teeters on the brink of a recession, generating income through investing can be a challenging task, especially during times of uncertainty. With the current state of the economy, you may be looking for ways to supplement an investment portfolio. Index options provide unique advantages and risk mitigation over stock and ETF options with income-generating options strategies. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at popular strategies for generating income and tips for managing risk and maximizing profits. Whether you are a seasoned options trader or just starting out, this post will provide you with valuable insights on how to generate income using index options in 2023.
Index options have several advantages over stock and ETF options that make them an attractive choice for the income-generating strategies that we’ll explore in this post. Index options such as the ones listed on the Nasdaq-100 Index (NDX) and the Nasdaq-100 Volatility Index (VOLQ) are:
- European Style & Cash Settled – They can only be exercised on the expiration date and are not subject to early exercise or assignment. This will can reduce the overall risk of an income strategy.
- Cash Settled – Short options contracts used in income strategies typically take on the obligation to buy or sell the underlying at the strike price upon expiration. The Cash Settled nature of index options removes this condition and profits and losses and simply settles in cash upon expiration.
- Section 1256 Contract – These have a potentially favorable tax treatment with 60% of profits taxed at long term and 40% at short term. This lowers the effective rate in a taxable account, compared to a similar strategy using ETF options.
Strategies for Generating Income using Index Options
One of the most popular strategies using index options is to generate income from selling options contracts. When you sell an options contract, you receive a premium in exchange for taking on the obligation to sell or buy the underlying asset at a specific price. This premium can serve as a source of consistent income, especially if you follow trading and risk management best practices.
Credit Vertical Spreads - Selling credit spreads is the most popular index options strategy. A Credit Spread is constructed by selling an option with a strike price close to the current price and buying another with a further Out-of-the-Money (OTM) strike price on the same expiration date. The goal is to receive a premium for selling the spread, with the hope that the options expire worthlessly and keep the premium as profit. This strategy typically has a high probability of profit, but the trade-off is taking on a risk that is typically higher than the potential reward. Based on our research, the optimal credit spread is constructed with 45 Days to Expiration, selling the 50 Delta Call or Put and buying the 25 Delta Call or Put.
An example of an Optimal Bullish Credit Spread when the Nasdaq-100 Micro Index Option (XND) is trading @ $123.63
Selling a March $123/$111 Put Vertical Credit Spread @ $4.93 Credit
Our Optimal Credit Spread is 45 Days to Expiration
Selling the 50 Delta Call or Put
Buying the 25 Delta Call or Put
Max Risk of $707
Max Reward of $493
Probability of Profit of 61%.

Naked Puts - Selling naked puts is another popular strategy in index options trading. This involves selling a put option without the required capital to purchase the underlying. The goal of selling naked puts is to collect the premium and take advantage of the time decay of the option. By selling a naked put will typically produce income levels that are significantly higher than a credit spread but also takes on very substantial risk. A naked short put is exposed to unlimited downside risk if the underlying security declines significantly. It is important to carefully assess technical levels and macro-economic activity with this type of strategy. Based on our research, the optimal credit spread is constructed with 30 Days to Expiration and selling the 40 Delta Put.
An example of an Optimal Bullish Naked Put when XND is trading @ $123.63
Selling a March $121 Put @ $8.00 Credit
Max Risk of $11,300
Max Reward of $800
Probability of Profit of 73%.

Short Strangle - A short strangle involves selling both a call option and a put option on the same expiration date with different strike prices. The goal of this strategy is to generate income by collecting premiums from the options sold, with the hope that the underlying asset will stay within a certain range and the options will expire worthless. However, short strangles involve taking on significant risk, as there is unlimited loss potential if the underlying asset moves too far away from the strike price(s). Based on our research, the optimal Short Strangle is constructed with 45 Days to Expiration and selling the 30 Delta Call and Put.
An example of an Optimal Short Strangle when XND is trading @ $123.63
Selling a March $114/$130 Strangle @ $6.98 Credit
Max Risk of Unlimited
Max Reward of $698
Probability of Profit of 63%.

When it comes to generating income with index options, risk management is arguably as important as the strategies you choose. It’s crucial to understand the potential risks involved and trade size that is appropriate for your portfolio. One of the key principles of risk management in options trading is to have a clear understanding of your risk tolerance. We suggest that the max risk of any options income strategy should not account for more than 2% of your total account value. This means that in a hypothetical $100,000 portfolio, the Max Risk that you should take on any single strategy should be less than $2,000. With a limited risk strategy, it should be easy to calculate the # of contracts. It gets trickier with strategies with unlimited risk. We suggest using the 3 Standard Deviation rule for strategies with unlimited risk. That is, if the underlying were to move 3 SD’s away from the current price, based on your trade size, it should not exceed more than 2% of your total account value. By monitoring volatility and adjusting your options positions accordingly, you can maximize your profits while minimizing your risk. Finally, it's important to have a well-defined exit strategy in place when trading these strategies.
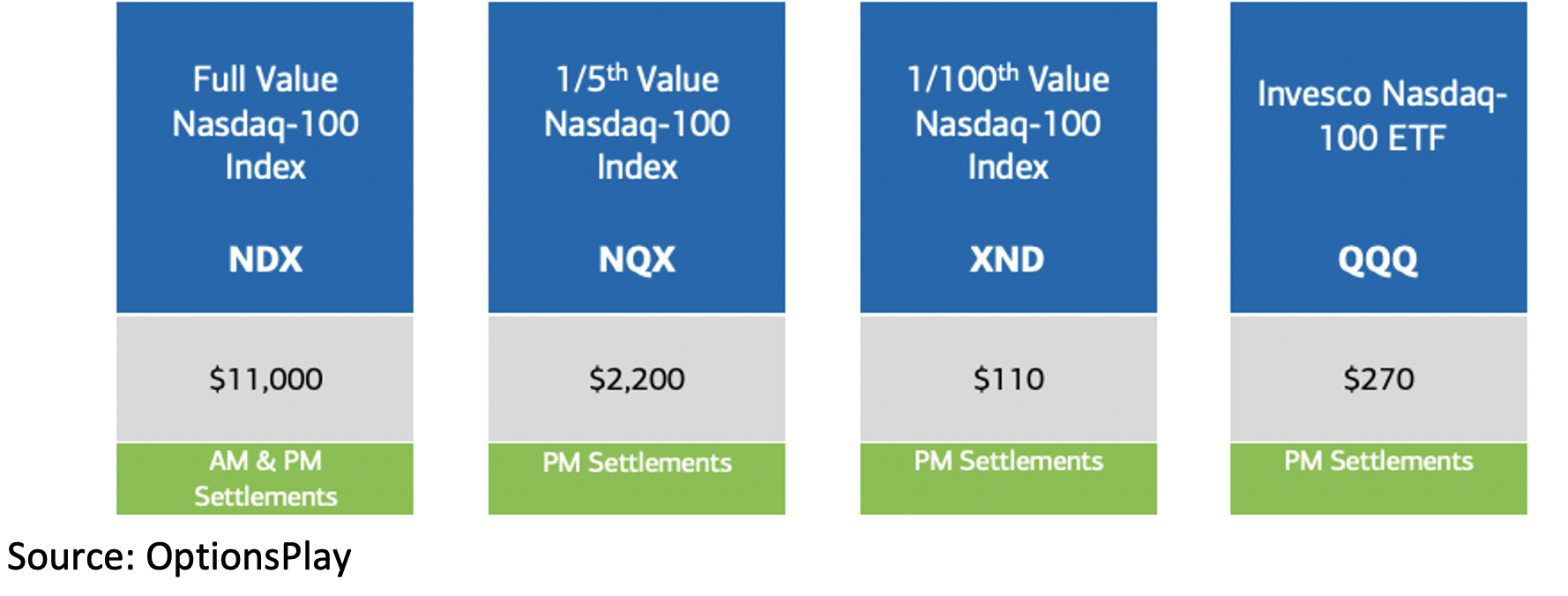
While there are many benefits to index options, they can be out of reach for retail traders due to their large contract sizes. With the NDX currently at $11,000, 1 contract would represent 100x the index of NDX, a $1.1 million contract, typically too large retail traders. However, indexes like the Nasdaq-100 Micro Index (XND) provide a solution to this.
The Nasdaq-100 Micro Index (XND)
The Nasdaq-100 Micro Index (XND) is based on 1/100th of the full value NDX. It tracks the performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index just like NDX, but the notional value of the exposure is 1/100th the size. Ideal for retail traders to access the same advantages of index options with a contract size that is better suited for smaller portfolios.
Image: Nasdaq-100 Index and ETF Options
In conclusion, generating income with index options can be a powerful tool for investors as we approach uncertain recessionary times. By understanding the role of volatility, using a combination of options strategies, and properly managing risk, you can learn to generate a consistent income stream with tax advantages and risk mitigation using index options such as the ones listed on the NDX.
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.
